- What is a Commodity Derivatives Market?
A commodity market is a marketplace for buying, selling, and trading raw materials or primary products.
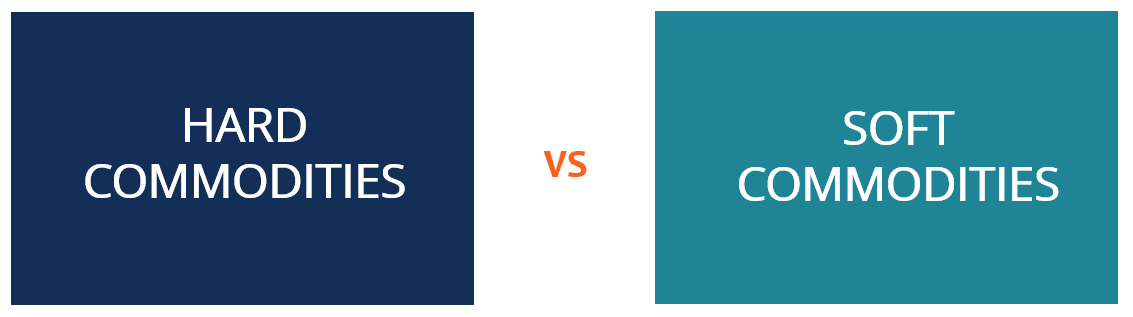
Commodities are often split into two broad categories: hard and soft commodities. Hard commodities include natural resources that must be mined or extracted—such as gold, rubber, and oil, whereas soft commodities are agricultural products or livestock—such as corn, wheat, coffee, sugar, soybeans, and pork.
- How does the Commodities Markets work?
For spot markets, buyers and sellers exchange cash for immediate delivery of the physical product. In derivatives markets, buyers and sellers exchange cash for the right to future delivery of that product. Oftentimes, derivatives holders will roll over or close out their positions before delivery can happen. Forwards trade over the counter and are customized between counterparties. Futures and options are listed on exchanges and have standardized contracts that are more highly regulated.
Derivatives markets involve forwards, futures, and options. Forwards and futures are derivatives contracts that use the spot market as the underlying asset
- What do Commodities Traders Do?
Depending on what type of trader you are, you will use this market for different purposes, for instance, buying or selling a physical product, hedging, speculating, or arbitraging.
Commodities markets allow producers and consumers of commodity products to gain access to them in a centralized and liquid marketplace. These market actors can also use commodities derivatives to hedge future consumption or production. Speculators, investors, and arbitrageurs also play an active role in these markets.
Certain commodities, such as precious metals, have been thought of to be a good hedge against inflation, and a broad set of commodities as an alternative asset class can help diversify a portfolio. Because the prices of commodities tend to move in opposition to stocks, some investors also rely on commodities during periods of market volatility.
In the past, commodities trading required significant amounts of time, money, and expertise, and was primarily limited to professional traders. Today, there are more options for participating in the commodity markets.
- The major exchanges in the world
- The major exchanges in the U.S., which trade commodities, are domiciled in Chicago and New York with several exchanges in other locations within the country. The Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) was established in Chicago in 1848. Commodities traded on the CBOT include corn, gold, silver, soybeans, wheat, oats, rice, and ethanol.
- The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) trades commodities such as milk, butter, feeder cattle, cattle, pork bellies, lumber, and lean hogs.
- The New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) trades commodities on its exchange such as oil, gold, silver, copper, aluminum, palladium, platinum, heating oil, propane, and electricity.
- Formerly known as the New York Board of Trade (NYBOT), ICE Futures U.S. commodities include coffee, cocoa, orange juice, sugar, and ethanol trading on its exchange.
- The London Metal Exchange and Tokyo Commodity Exchange are prominent international commodity exchanges.

Source: Investopedia



![[WHEAT] Top 10 Countries That Produce The Most Wheat](https://straitsvietnam.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/218966-300x200.jpg)
![[SOYBEAN OIL] Top 5 Factors Influencing On Soybean Oil Prices](https://straitsvietnam.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/DAU-DAU-TUONG-300x198.jpg)
